Agenda
DRF provides several generic views. RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView is one among them.
In this post, we will see when RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView should be preferred over vanilla APIView. We will also see several hook points provided by RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView.
Setup
We will use Django polls app as our reference throughout this post. I assume you are familiar with Question and Choice model used in polls app.
Let’s assume we have a class based apiview to see detail of a question. This view also allows editing and deleting a question. The serializer looks like the following:
# polls/serializers.py
class QuestionDetailPageSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
was_published_recently = serializers.BooleanField(read_only=True)
class Meta:
model = Question
fields = '__all__'
The apiview looks like the following:
from rest_framework.views import APIView
class QuestionDetailView(APIView):
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=kwargs['question_id'])
serializer = QuestionDetailPageSerializer(question)
return Response(serializer.data)
def patch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=kwargs['question_id'])
serializer = QuestionDetailPageSerializer(question, data=request.data, partial=True)
if serializer.is_valid():
question = serializer.save()
return Response(QuestionDetailPageSerializer(question).data)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
def delete(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=kwargs['question_id'])
question.delete()
return Response("Question deleted", status=status.HTTP_204_NO_CONTENT)
The urlpattern for this apiview is:
# polls/urls.py
path('questions/<int:question_id>/', apiviews.QuestionDetailView.as_view(), name='question_detail_view')
Urlpattern of root URLconf file is:
# mysite/urls.py
path('api/polls/', include('polls.urls'))
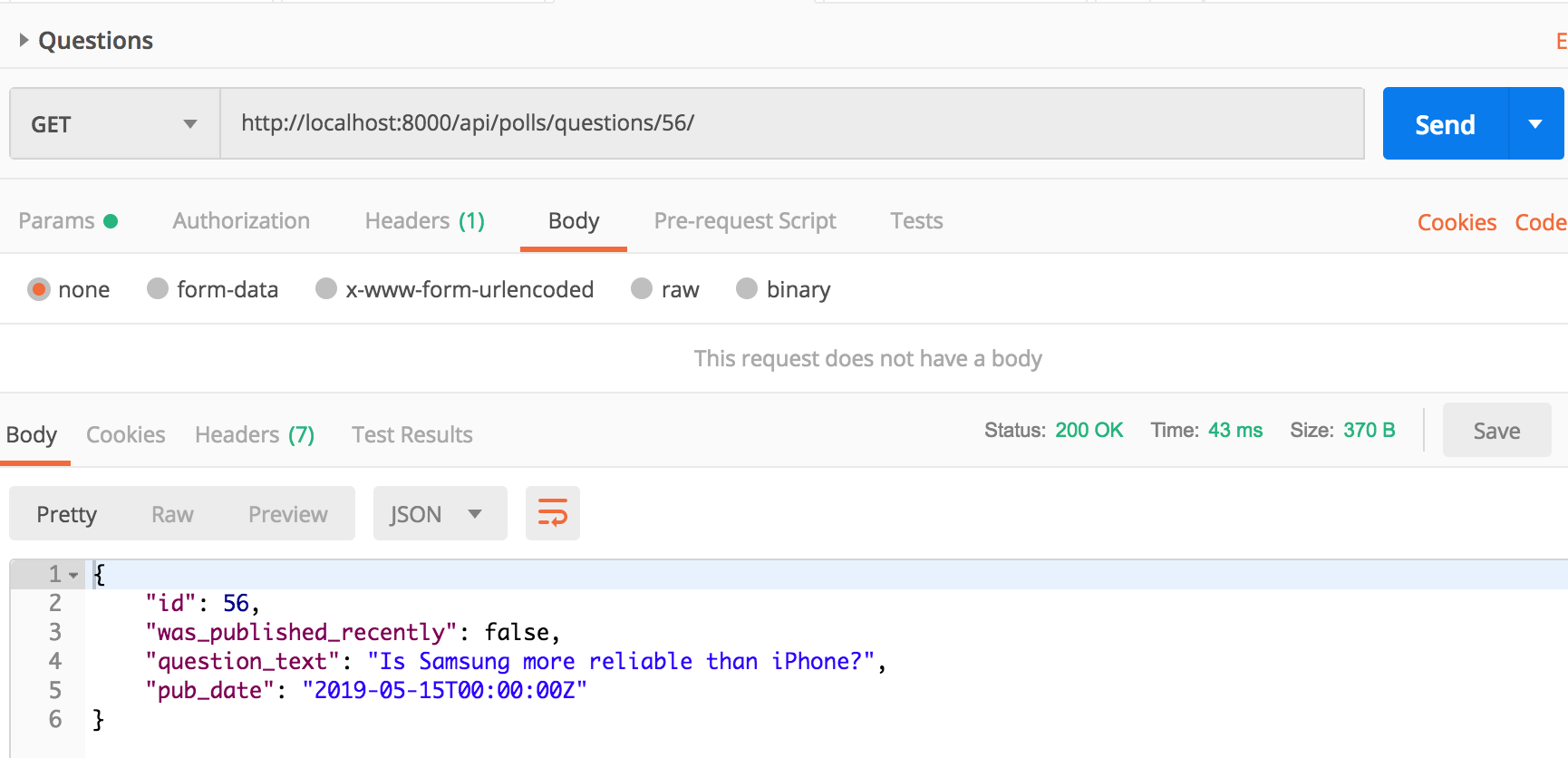
Api request to get question detail look like:
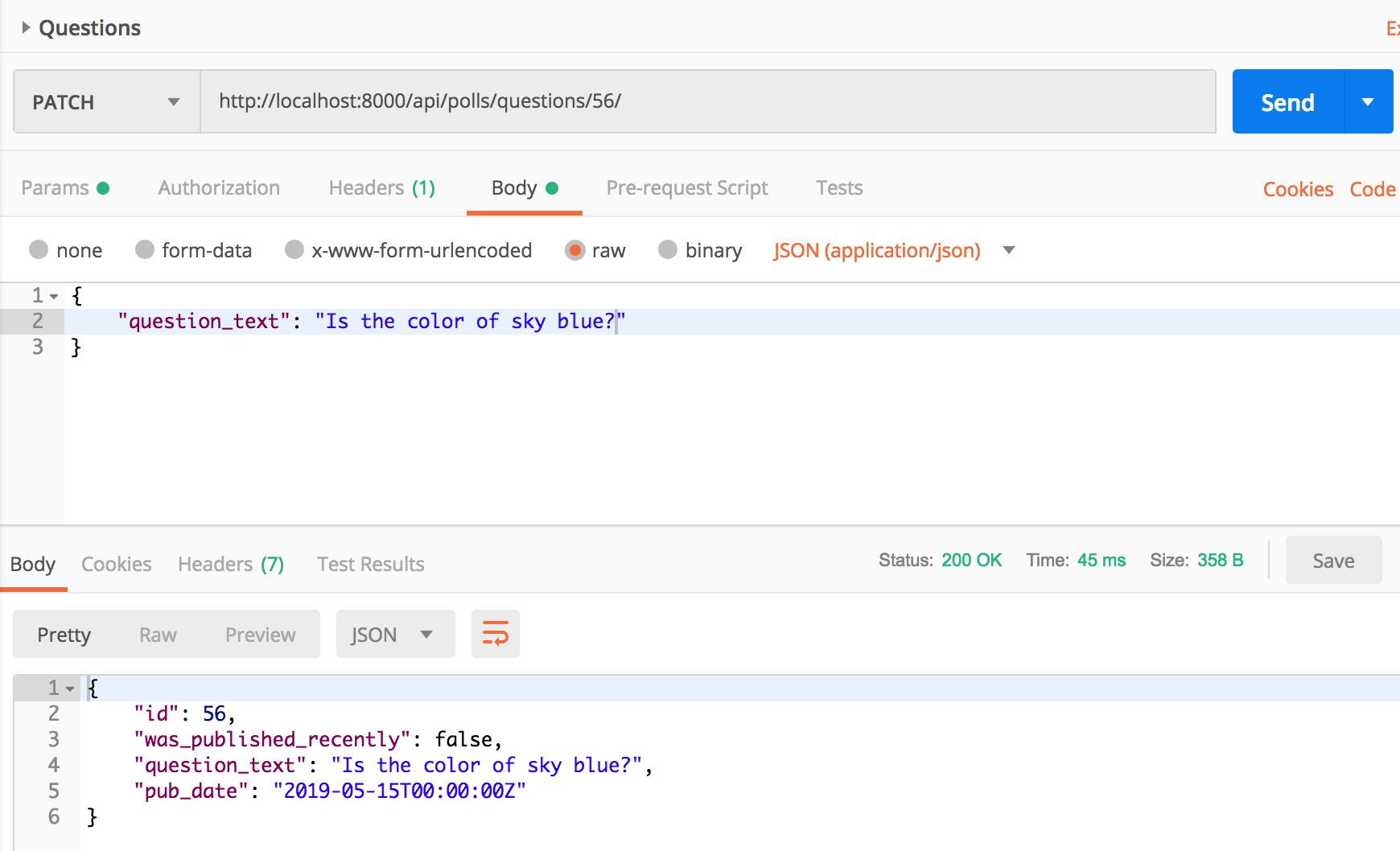
Api request to update a question look like the following. It is a PATCH request.
Side Note: Read our detailed post on adding an api layer to Django polls app.
RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView
Our view has a very commonly occuring pattern where we want to see detail of a model instance, want to edit a model instance and delete a model instance. We had to provide a get(), patch() and delete() implementation to achieve this.
RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView provides a default implementation of get(), patch() and delete(). RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView requires two mandatory attributes which are serializer_class and queryset. There is another optional attribute called lookup_url_kwarg which might be needed depending on your url pattern.
Let’s modify the QuestionDetailView to use RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView.
class QuestionDetailView(RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
serializer_class = QuestionDetailPageSerializer
lookup_url_kwarg = 'question_id'
queryset = Question.objects.all()
We had to add lookup_url_kwarg because our url pattern uses question_id as a url keywork argument.
Had our url been path('questions/<int:id>/', apiviews.QuestionDetailView.as_view(), name='question_detail_view'), i.e used keyword argument id instead of question_id then there was no need to specify lookup_url_kwarg on QuestionDetailView. In such case, QuestionDetailView would change to:
class QuestionDetailView(RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
serializer_class = QuestionDetailPageSerializer
queryset = Question.objects.all()
GET, PATCH and DELTE api request will keep working as they were working with APIView. Notice how we were able to avoid get(), patch() and delete() on QuestionDetailView.
Suppose we only want the detail view of questions published in last two days to be visible. We want a 404 to be raised if the question hasn’t been published in last two days. We will have to override get_queryset() in that case.
from django.utils.timezone import now
from datetime import timedelta
class QuestionDetailView(RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
serializer_class = QuestionDetailPageSerializer
lookup_url_kwarg = 'question_id'
def get_queryset(self):
last_two_days = now() - timedelta(days=2)
return Question.objects.filter(pub_date__gt=last_two_days)
If you want to use different serializers for different methods, you will have to override get_serializer_class. Our post on ListCreateAPIView discusses overriding get_serializer_class.
Suppose we want to use question_text in url instead of id. We will change our urlpattern to:
path('questions/<str:question_text>/', apiviews.QuestionDetailView.as_view(), name='question_detail_view')
We will need to use lookup_field attribute of RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView in such case.
class QuestionDetailView(RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
serializer_class = QuestionDetailPageSerializer
lookup_url_kwarg = 'question_text'
lookup_field = 'question_text'
def get_queryset(self):
last_two_days = now() - timedelta(days=2)
return Question.objects.filter(pub_date__gt=last_two_days)
Stay tuned for our next post of the series which is on DRF Viewset.
Thank you for reading the Agiliq blog. This article was written by Akshar on May 16, 2019 in API , django , drf .
You can subscribe ⚛ to our blog.
We love building amazing apps for web and mobile for our clients. If you are looking for development help, contact us today ✉.
Would you like to download 10+ free Django and Python books? Get them here
