What is Hasura ?
- It’s opensource and has good community support.
- Hasura is a GraphQL engine that creates a GraphQL api from the PostgreSQL database schema.
- We can use exising database or use a new one
- Powerful authorization engine
- Can safely be used by frontend apps directly.
Running the Hasura GraphQL engine on Docker
Docker is a containarization tool that helps containerizing the app. We use docker to get started with the GraphQL.
Installing docker on ubuntu
- To install the docker on ubuntu using
snappackage manager, Just run the below command.
sudo snap install docker
Docker compose file for Hasura
version: '3.6'
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:12
restart: always
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: pgsecret
graphql-engine:
image: hasura/graphql-engine:latest
ports:
- "4400:8080"
depends_on:
- "postgres"
restart: always
environment:
HASURA_GRAPHQL_DATABASE_URL: postgres://postgres:pgsecret@postgres:5432/postgres
HASURA_GRAPHQL_ENABLE_CONSOLE: "true"
HASURA_GRAPHQL_ADMIN_SECRET: "hasurasecret"
volumes:
db_data:
-
HASURA_GRAPHQL_ADMIN_SECRETis for security. We need pass the headerx-hasura-admin-secretto access the endpoint. -
Let’s create the containers for Hasura GraphQL engine and PostgreSQL database with the below command.
docker-compose up -d
- We should be on the same directory where the docker compose file resides to make it work.
- To confirm docker is running Hasura GraphQL and PostgreSQL run the command
docker ps. It will show the output like below.
ubuntu@agiliq:~$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
2fede48be420 hasura/graphql-engine:latest "graphql-engine serve" About a minute ago Up Less than a second 0.0.0.0:4400->8080/tcp ubuntu_graphql-engine_1
31c1193074f6 postgres:12 "docker-entrypoint.s…" About a minute ago Up 7 seconds 5432/tcp ubuntu_postgres_1
From the above output we can see that both the containers are running. We can access the Hasura GraphQL Engine at 0.0.0.0:4400. Now, you will see the screen like below.
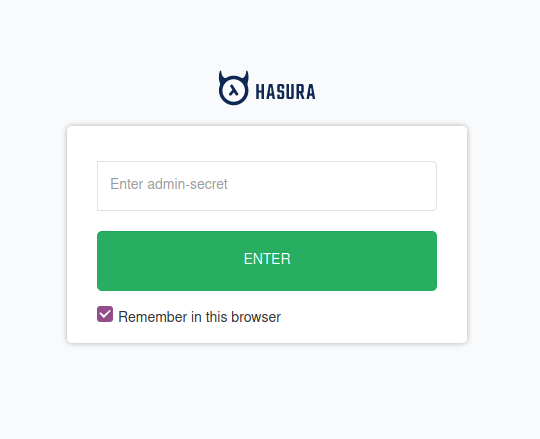
Login to Hasura GraphQL engine with password hasurasecret. We configured it using HASURA_GRAPHQL_ADMIN_SECRET environment variable. We can see the screen like below after successfully login to it.
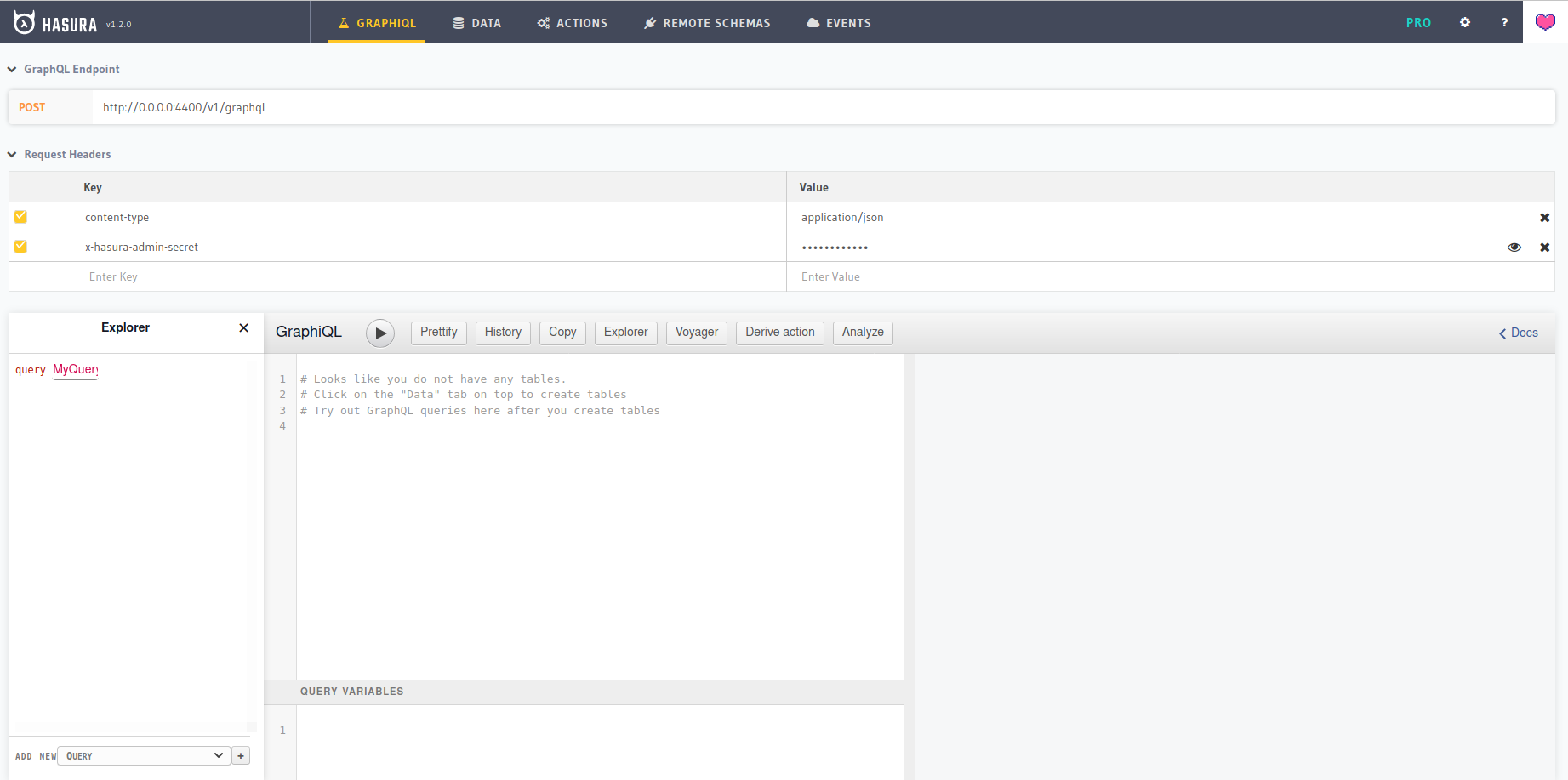
Note: Docker compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. To know more about it visit official website.
Creating the database schema
- We don’t have any tables and data in the database so, let’s create the database schema from the
Hasura Dashboarditself. - We can find the
DATAon top navigation menu. Just click on it, it will take us to databaseschemapage. Click on “Add Table” button to create a table like below.
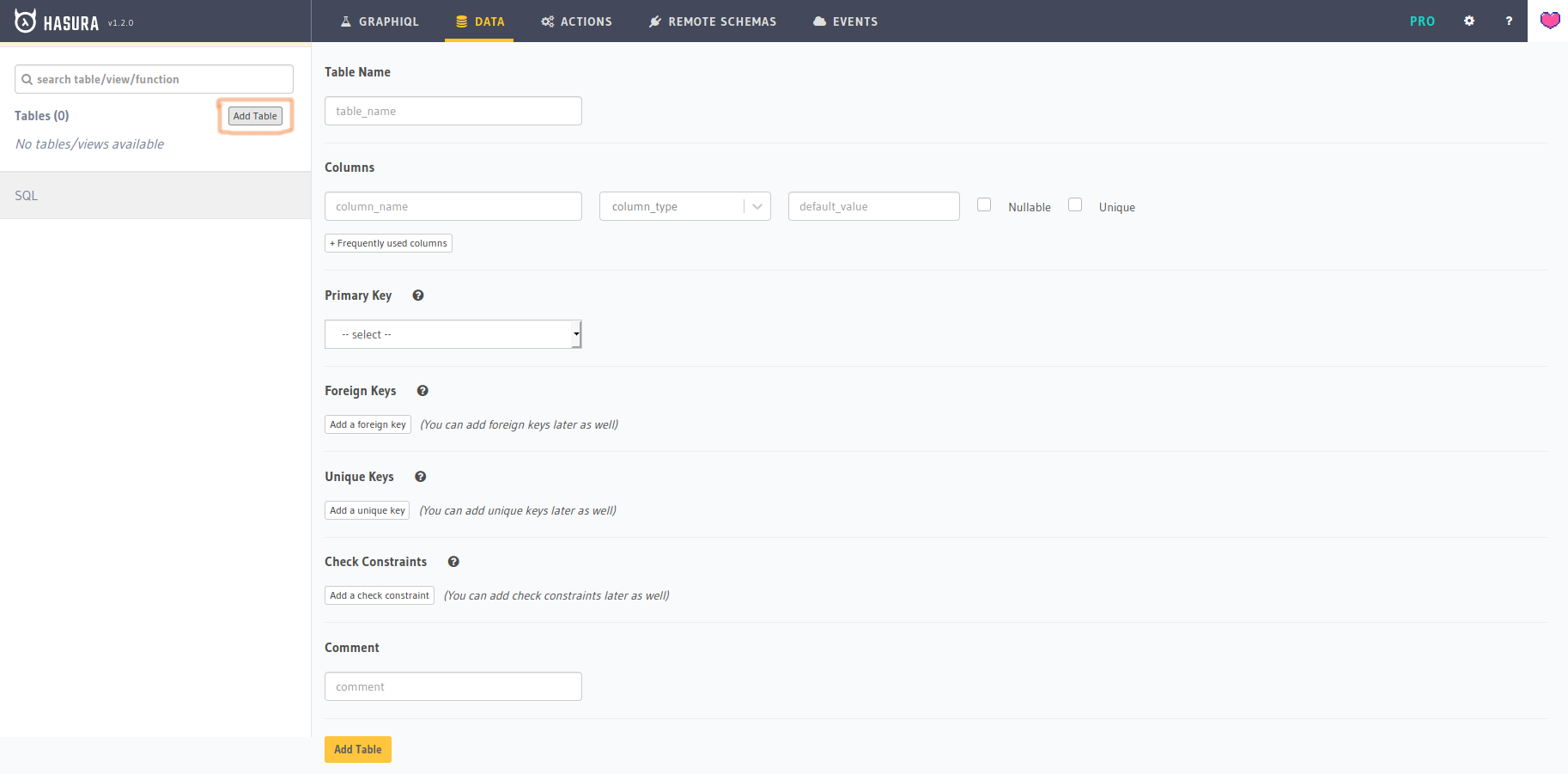
- Let’s consider the scenario of
authorandarticle. Author can write an article and article can associate with at most one author.
Database tables
postgres=# \d+ public.author;
Table "public.author"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+---------+-----------+----------+------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------
id | integer | | not null | nextval('author_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |
name | bpchar | | not null | | extended | |
Indexes:
"author_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (id)
Referenced by:
TABLE "article" CONSTRAINT "article_author_id_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (author_id) REFERENCES author(id) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE
Access method: heap
postgres=# \d+ public.article;
Table "public.article"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description
-----------+-------------------+-----------+----------+-------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------
id | integer | | not null | nextval('article_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |
title | character varying | | not null | | extended | |
content | text | | not null | | extended | |
author_id | integer | | not null | | plain | |
Indexes:
"article_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (id)
Foreign-key constraints:
"article_author_id_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (author_id) REFERENCES author(id) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE
Access method: heap
Mutation Query on Hasura GraphQL Engine
Let’s create a query to insert the data into the author table.
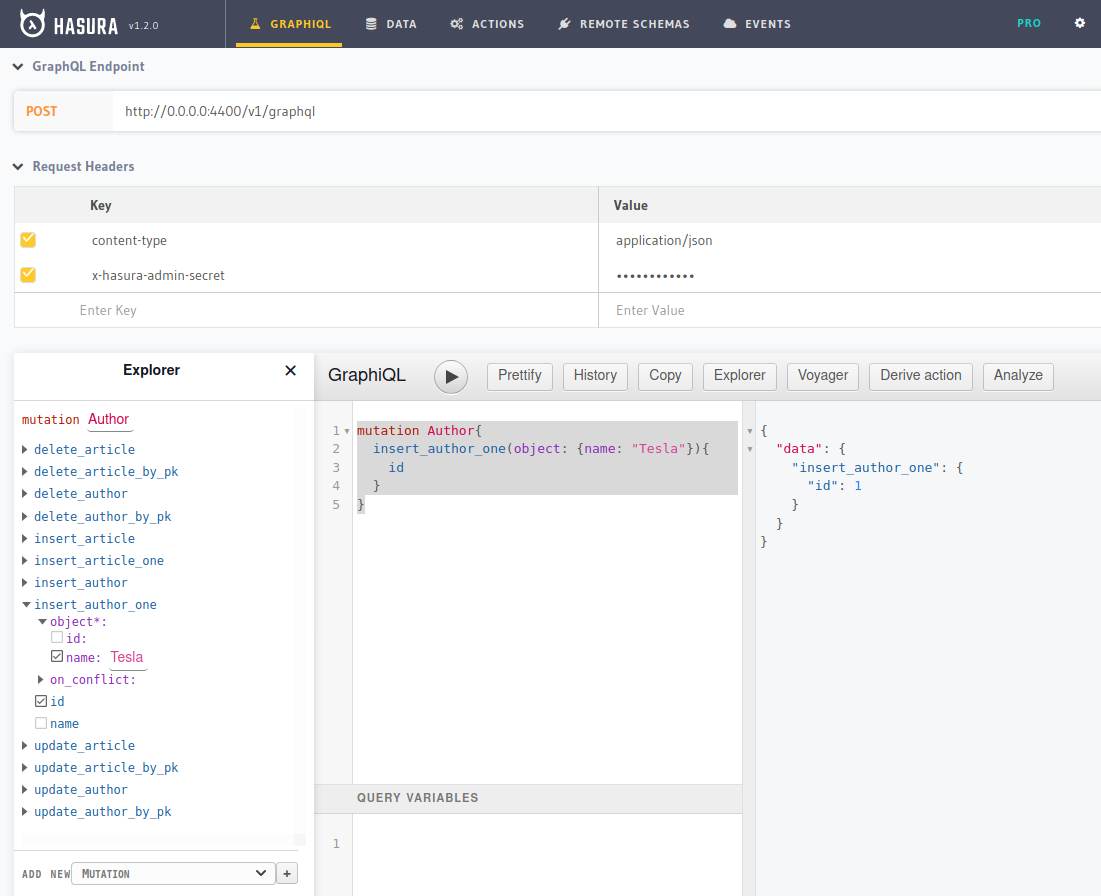
Query:
mutation Author{
insert_author_one(object: {name: "Tesla"}){
id
}
}
cURL:
curl 'http://0.0.0.0:4400/v1/graphql' -H 'content-type: application/json' -H 'x-hasura-admin-secret: hasurasecret' -H 'Origin: http://0.0.0.0:4400' --data '{"query":"mutation Author{\n insert_author_one(object: {name: \"Einstein\"}){\n id\n }\n}","variables":null,"operationName":"Author"}'
Output:
{"data":{"insert_author_one":{"id":2}}}
retrieve query on Hasura GraphQL Engine
Let’s insert the data into the database manually through the Hasura GraphQL dashboard. We need to configure the relationships before writing the query for related objects.
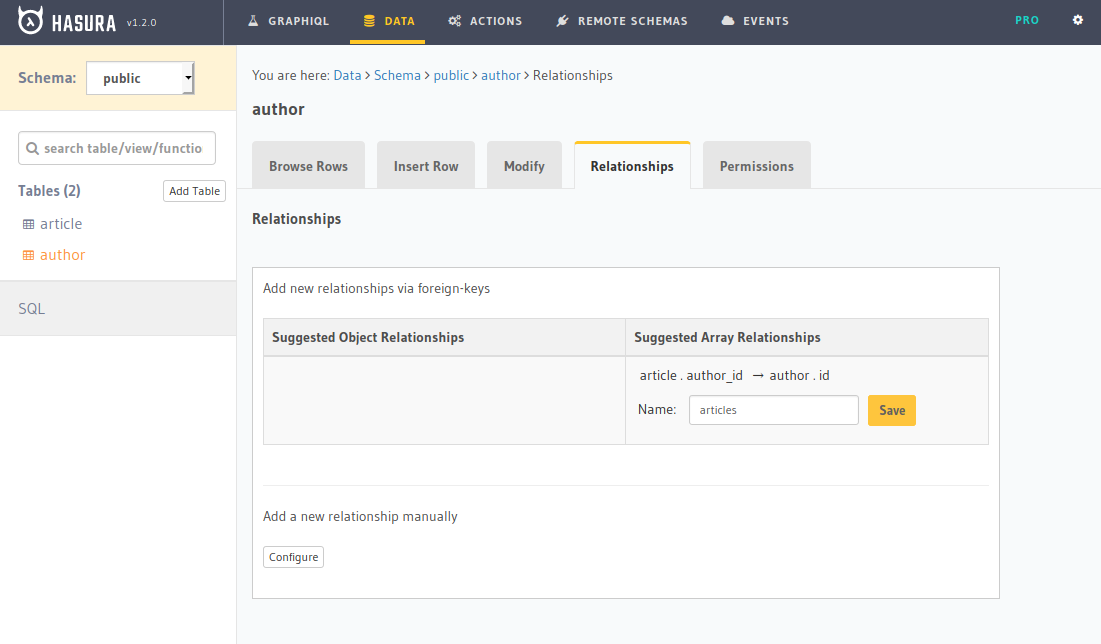
Now, we are ready. Let’s write the query
query authors_articles {
author {
id
name
articles{
id
title
}
}
}
cURL:
curl 'http://0.0.0.0:4400/v1/graphql' -H 'content-type: application/json' -H 'x-hasura-admin-secret: hasurasecret' -H 'Origin: http://0.0.0.0:4400' -H 'Connection: keep-alive' --data '{"query":"query authors_articles {\n author {\n id\n name\n articles{\n id\n title\n }\n }\n}\n","variables":null,"operationName":"authors_articles"}'
Output:
{
"data": {
"author": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Tesla",
"articles": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "tesla book"
}
]
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Einstein",
"articles": []
}
]
}
}
Hasura GraphQL engine made it very simple to create the GraphQL api with less effort and more functionality. That’s it folks, We can do more with Hasura GraphQL engine.
Reference: https://hasura.io/docs/1.0/graphql/manual/index.html
Thank you for reading the Agiliq blog. This article was written by Anjaneyulu Batta on May 4, 2020 in GraphQL , PostgreSQL .
You can subscribe ⚛ to our blog.
We love building amazing apps for web and mobile for our clients. If you are looking for development help, contact us today ✉.
Would you like to download 10+ free Django and Python books? Get them here
